Contractual chain
It is common practice on construction projects to have more than one set of parallel contractual arrangements in place. On the one hand there is the main contract between the employer (client) and the main contractor; on the other hand, there is the sub-contract between the main contractor and the sub-contractor or sub-contractors. Each of these contractual arrangements is regarded as a link in the overall contractual chain.
One of the features of the contractual chain is the privity of contract. This means that the rights and obligations contained in the contract apply only to those who are a party to it. So, the main contract between the client and main contractor does not involve the sub-contractor who is therefore not liable contractually to the client for any actual breach of contract. The subcontractor therefore cannot claim against the client for say, poor working conditions or for retention monies held by the main contractor which have yet to be received. The sub-contractor must claim against the main contractor.
Likewise, the sub-contract between the main contractor and the sub-contractor does not involve the client. If the client wishes to claim against the sub-contractor, whether for the latter committing breach of contract or for defective work, the claim must be redressed by the main contractor. In such cases, the sub-contractor is liable to the main contractor.
There is usually no privity of contract between the client and the sub-contractor (whether nominated or domestic). So, for whatever breach of contract, fault or misdemeanour, the sub-contractor is not usually liable to the client. Which means the client cannot claim against the sub-contractor but must recover any due costs from the main contractor (with whom they have privity of contract). The main contractor in turn recovers the costs from the sub-contractor. This amounts to a chain of liability, where recovering costs requires either going up or down the contractual chain.
Problems can arise where the chain involves a weak link. For example, if the terms of the main contract and the sub-contract are not comparable, are incompatible or are just different, relying on the chain of liability could be problematic. There may be a break in the chain which would see the sub-contractor unable to recover any payments or compensation which are rightly due.
On large or complex projects, responsibility and performance generally cascades down the supply chain to a plethora of suppliers, some of whom may be entirely unknown to management at the top of the chain.
For more information see: Supplier and Supply chain.
NB Collateral warranties are agreements which are associated with another 'primary' contract. They provide for a duty of care to be extended by one of the contracting parties to a third party who is not party to the original contract. A typical example would be where an architect of a development owes a duty of care to an occupier of the development in so far as any subsequent defects which may arise are concerned. Privity of contract rules would prevent any liability arising between the architect and occupier without the existence of a collateral warranty.
For more information see: Collateral warranty.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
Featured articles and news
Sir John Betjeman’s love of Victorian church architecture.
Exchange for Change for UK deposit return scheme
The UK Deposit Management Organisation established to deliver Deposit Return Scheme unveils trading name.
A guide to integrating heat pumps
As the Future Homes Standard approaches Future Homes Hub publishes hints and tips for Architects and Architectural Technologists.
BSR as a standalone body; statements, key roles, context
Statements from key figures in key and changing roles.
ECA launches Welsh Election Manifesto
ECA calls on political parties 100 day milestone to the Senedd elections.
Resident engagement as the key to successful retrofits
Retrofit is about people, not just buildings, from early starts to beyond handover.
Plastic, recycling and its symbol
Student competition winning, M.C.Esher inspired Möbius strip design symbolising continuity within a finite entity.
Do you take the lead in a circular construction economy?
Help us develop and expand this wiki as a resource for academia and industry alike.
Warm Homes Plan Workforce Taskforce
Risks of undermining UK’s energy transition due to lack of electrotechnical industry representation, says ECA.
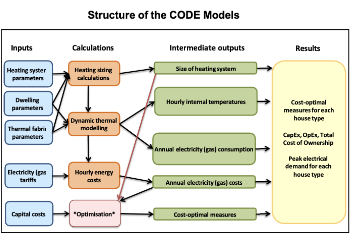
Cost Optimal Domestic Electrification CODE
Modelling retrofits only on costs that directly impact the consumer: upfront cost of equipment, energy costs and maintenance costs.
The Warm Homes Plan details released
What's new and what is not, with industry reactions.
Could AI and VR cause an increase the value of heritage?
The Orange book: 2026 Amendment 4 to BS 7671:2018
ECA welcomes IET and BSI content sign off.